Sex Differences in Pubertal Circadian and Ultradian Rhythmic Development Under Semi-Naturalistic Conditions
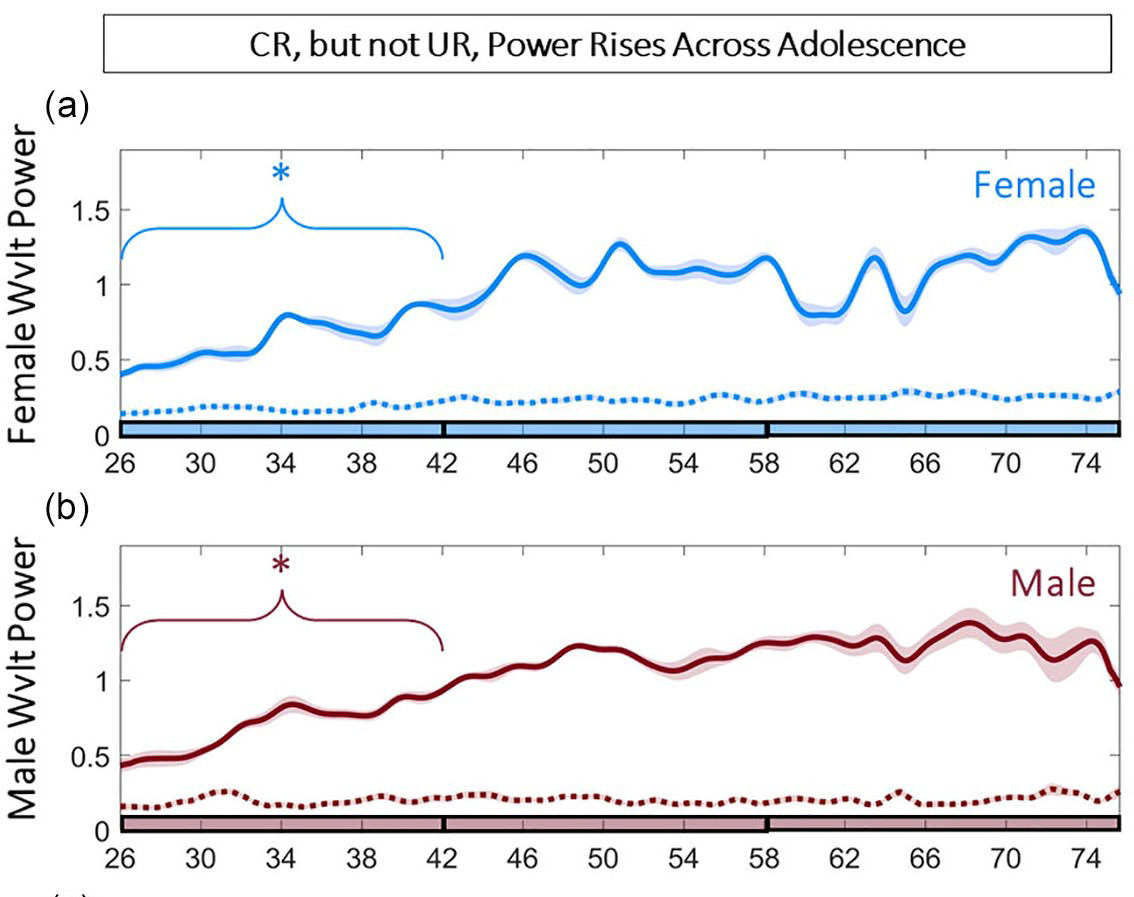
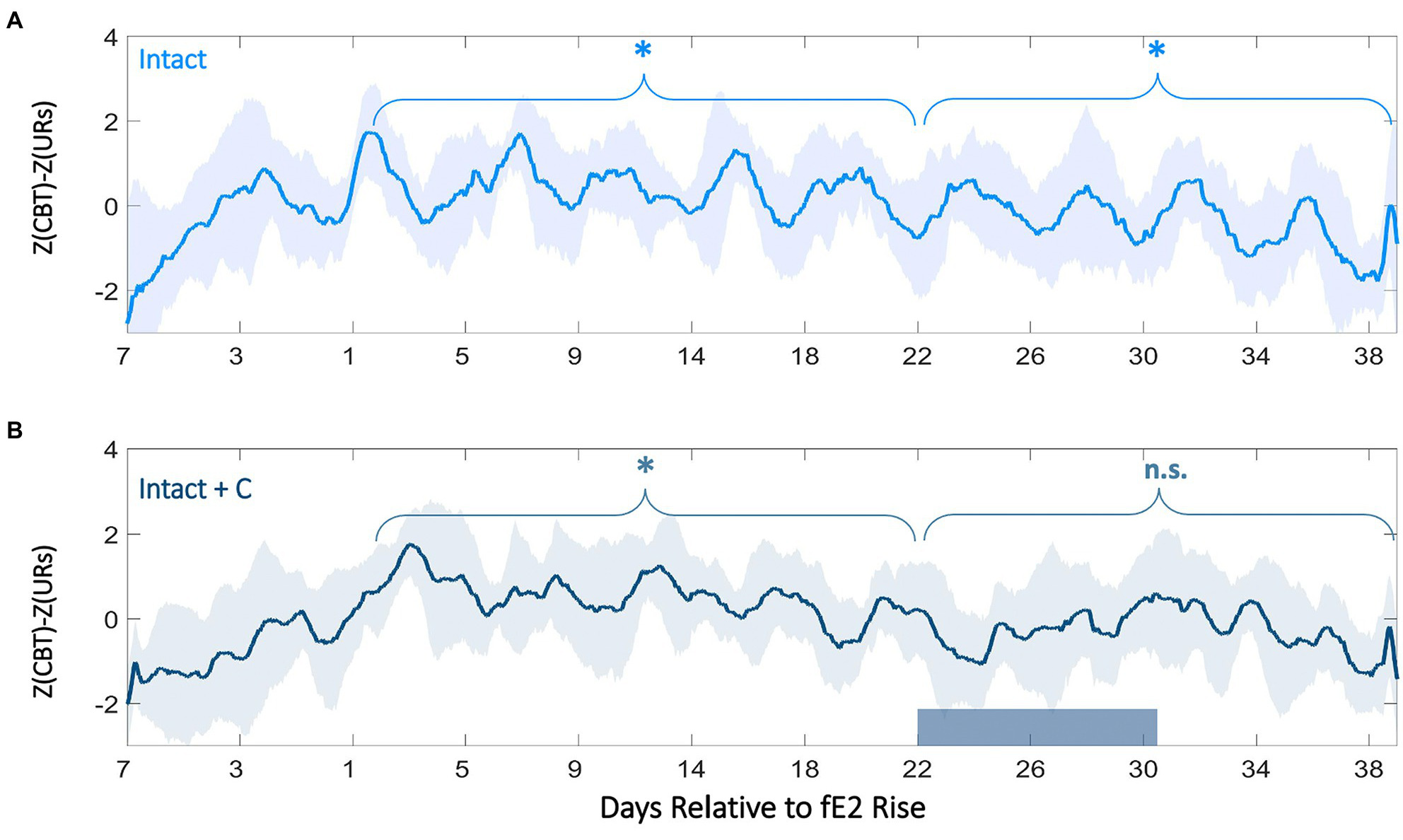
Biological rhythms in core body temperature (CBT) provide informative markers of adolescent development under controlled laboratory conditions. However, it is unknown whether these markers are preserved under more variable, semi-naturalistic conditions, and whether CBT may therefore prove useful in a real-world setting. To evaluate this possibility, we examined fecal steroid concentrations and CBT rhythms from pre-adolescence (p26) through early adulthood (p76) in intact male and female Wistar rats under natural light and climate at the Stephen Glickman Field Station for the Study of Behavior, Ecology and Reproduction. Despite greater environmental variability, CBT markers of pubertal onset and its rhythmic progression were comparable with those previously reported in laboratory conditions in female rats and extend actigraphy-based findings in males. Specifically, sex differences emerged in CBT circadian rhythm (CR) power and amplitude prior to pubertal onset and persisted into early adulthood, with females exhibiting elevated CBT and decreased CR power compared with males. Within-day (ultradian rhythm [UR]) patterns also exhibited a pronounced sex difference associated with estrous cyclicity. Pubertal onset, defined by vaginal opening, preputial separation, and sex steroid concentrations, occurred later than previously reported under lab conditions for both sexes. Vaginal opening and increased fecal estradiol concentrations were closely tied to the commencement of 4-day oscillations in CBT and UR power. By contrast, preputial separation and the first rise in testosterone concentration were not associated with adolescent changes to CBT rhythms in male rats. Together, males and females exhibited unique temporal patterning of CBT and sex steroids across pubertal development, with tractable associations between hormonal concentrations, external development, and temporal structure in females. The preservation of these features outside the laboratory supports CBT as a strong candidate for translational pubertal monitoring under semi-naturalistic conditions in females.
Grant, Azure D., Linda Wilbrecht, and Lance J. Kriegsfeld, Sex Differences in Pubertal Circadian and Ultradian Rhythmic Development Under Semi-Naturalistic Conditions, Journal of Biological Rhythms, (May 2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/07487304221092715